Raspberry Pi Pico W навчили цю машину обходити об'єкти
Створення робота-автомобіля, який уникає перешкод, може здатися однією з найскладніших збірок Raspberry Pi, з якими Ви можете працювати, з усіма двигунами, драйверами та датчиками, які вам потрібні. Але Карам Хаддад у своєму семихвилинному відео збірки ( Karam’s build video ) робить це так, що воно виглядає дуже легко.
Як це працює?
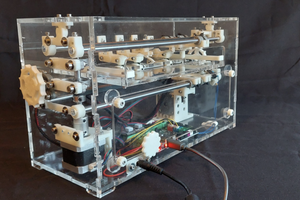
Мозком робота-автомобіля є Raspberry Pi Pico W, обраний саме через те, що він достатньо малий, щоб акуратно сховатися всередині шасі, але має необхідну обчислювальну потужність для обробки логічних задач керування, необхідних для навігації. Ультразвуковий датчик, встановлений на серводвигуні, дозволяє автомобілю вимірювати навколишнє середовище, знімаючи показання відстані в усіх напрямках. «Ця стіна знаходиться на відстані семи метрів, тому я повинен припинити рух до неї приблизно через 6,9 метра», — так казала сама собі машина. Робот навчений завжди віддавати перевагу руху вперед, коли шлях вільний, і оцінювати альтернативні шляхи лише тоді, коли виявлено об’єкт.

Регульоване джерело живлення постійного струму живить робота. Водій регулює напрямок і швидкість двигунів постійного струму, прикріплених до кожного колеса автомобіля.

Фізичне шасі автомобіля, включно з індивідуальними кріпленнями для двигунів і датчиків, було надруковано на 3D та склеєно гарячим способом.

Оу-оу, упс та вдосконалення
Караму довелося зробити декілька певних махінацій щоб усунути падіння напруги під час тестування, через що двигуни залишилися без достатньої потужності, але після цього робот був готовий до дорожніх випробувань навколо імпровізованої смуги перешкод. Виробник хотів би вивчити можливість інтеграції підключення до смартфону, що дозволить вам вручну керувати роботом.

Переходьте на GitHub аби отримати повний код, і поставьте відео Карама build video лайк на Ютубі.